The International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR)
Astronomers from The International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research, an international "centre of excellence" in astronomical science and technology based in Perth WA, have developed a new way of detecting active black holes.
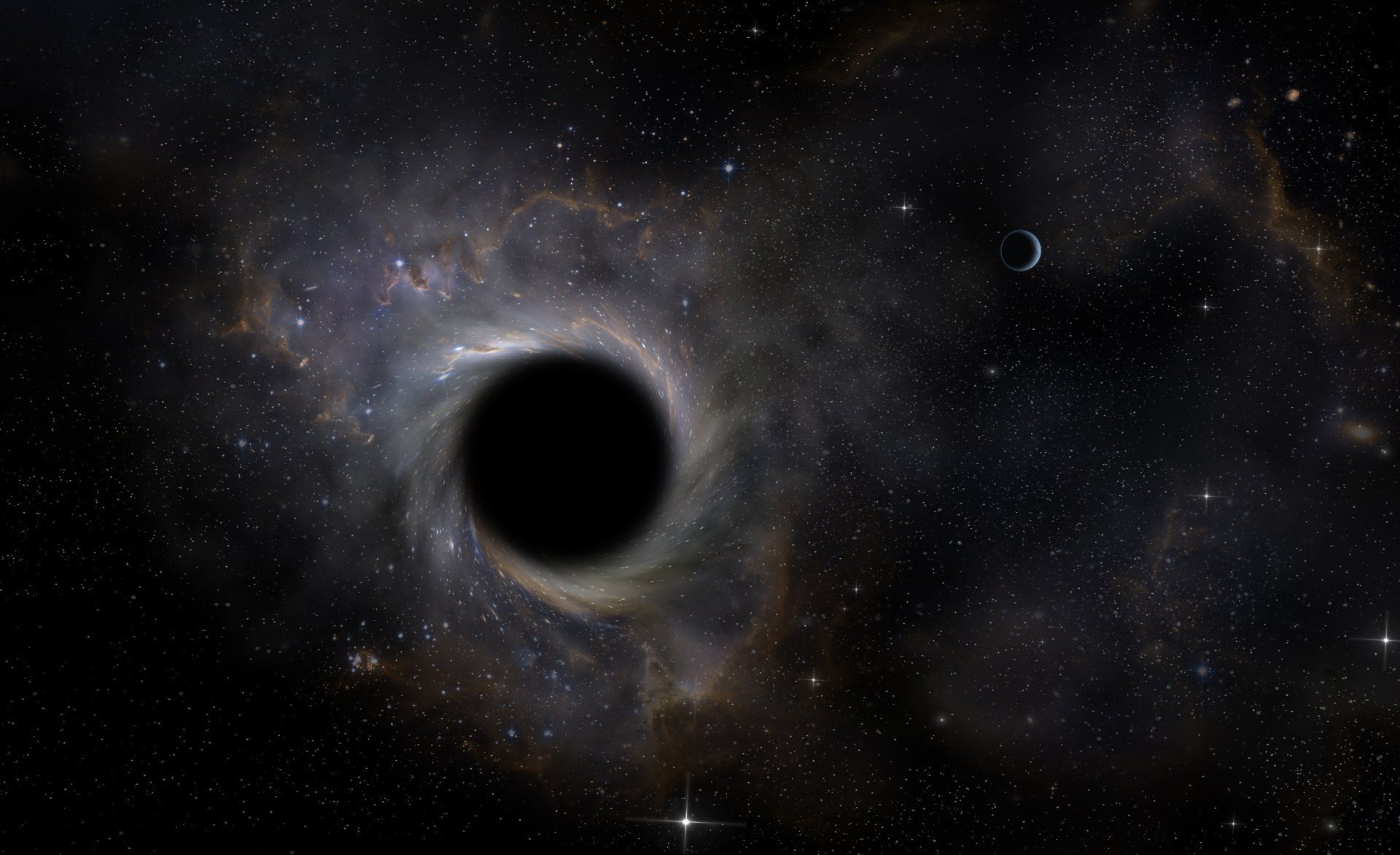

Astronomers have a new way of detecting active black holes in the Universe and measuring how much matter they are sucking in. The technique can be applied to millions of galaxies, searching for bright, supermassive black holes at the centre of the galaxies.
Lead author Jessica Thorne, a PhD student at the University of Western Australia node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research, said active black holes are typically found in the largest galaxies in the Universe.
“The black holes we’re looking for are between a million and a billion times more massive than our Sun,” she said. “As they suck in matter from around them, the matter gets super-heated because of friction and becomes very, very luminous. And when they’re active, these black holes can outshine the rest of the galaxy.”
Until now, identifying bright black holes has been challenging, with astronomers having to specifically look for them using complex methods unique to different types of telescopes. Instead, the new technique works on typical telescope observations that already exist for millions of galaxies.
“We can identify these active black holes and look at how much light they're emitting, but also measure the properties of the galaxy it is in at the same time,” Thorne said. “By doing both at once, we can have a better idea of exactly how the black hole is impacting its host galaxy.”
The researchers developed the new technique by using an algorithm called ProSpect to model emission from galaxies and black holes at different wavelengths of light. They then applied the method to almost half a million galaxies from Anglo-Australian Telescope’s DEVILS survey.
They also applied it to more than 200,000 galaxies from the GAMA survey, which brings together observations from six of the world’s best ground and space-based telescopes.
ICRAR-UWA astronomer Dr Sabine Bellstedt said scientists often fail to account for bright black holes in galaxies. “One of the reasons we’ve ignored them in the past is because it’s hard to find them all,” she said. “We don't really understand these bright black holes to incorporate them into our modelling with sufficient detail.”
Dr Bellstedt said the new technique is easier, more consistent and more thorough.
“It suddenly means we can look for active black holes in so many more places than we were able to before,” she said. “It’s going to help us search more galaxies, and look further back in time to the distant Universe.”
Supermassive black holes are thought to have a huge impact on how galaxies evolve.
“We think that an active black hole in a galaxy is able to decrease the amount of star formation really quickly and stop the galaxy from growing any further,” Thorne said. “It can effectively kill it.”
With observations from new telescopes such as the James Webb Space Telescope, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile, and the Square Kilometre Array in Australia and South Africa, astronomers may be able to apply the technique to millions of galaxies at once.
“It’s exciting to think about how many doors this has unlocked for the future,” Thorne said.
The International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) is a joint venture between Curtin University and The University of Western Australia with support and funding from the State Government of Western Australia.